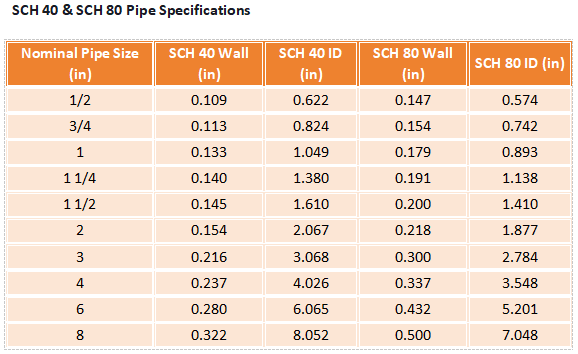
Pipe schedules show wall thickness and pressure limits. Each number represents a specific wall thickness. Engineers use these numbers to design safe and efficient piping systems.
Schedule 40 has thinner walls than Schedule 80. It suits systems with moderate pressure.
Schedule 80 walls are thicker than Schedule 40.They handle higher pressure and last longer. Choosing the correct schedule prevents leaks, bursts, and early failures.
Wall thickness affects strength, flow, and installation. Pipes with the same diameter but different schedules behave differently.
SCH 40 pipe features a lighter weight, which simplifies handling and installation. It also reduces installation time.
SCH 80 pipe offers greater strength, though its increased wall thickness results in higher weight. Proper support and careful handling are necessary to avoid damage.
Carbon steel pipe selection must consider fluid type and system requirements. Water supply pipe lines, HVAC systems, and drainage networks often rely on SCH 40 pipe.
It balances cost, weight, and pressure capacity. Chemical pipelines, industrial steam lines, and high-pressure pipe systems benefit from SCH 80 pipe. Its thicker walls resist erosion, corrosion, and mechanical stress.
Where SCH 40 and SCH 80 Are Used
Schedule 40 pipe is common in residential, commercial, and light industrial applications. The relatively low weight of SCH 40 pipe makes it more manageable during transport and installation. Its wall thickness supports low to moderate pressure while remaining manageable for installation.
Many engineers prefer SCH 80 pipe for chemical plants, high-pressure pipelines, and industrial systems. It resists wear, corrosion, and extreme pressure. Steam transport, chemical lines, and long-distance pipelines often select SCH 80 for reliability.
Temperature, fluid type, and pressure affect schedule choice. Hot steam lines often use SCH 80 pipe to prevent deformation. Cold water piping lines can safely use SCH 40 pipe.
Material selection also matters. Stainless steel SCH 80 offers extra corrosion resistance while maintaining pressure integrity. Proper planning reduces maintenance costs and extends the service life of pipe systems.
Flow rate and internal diameter are key considerations. The thinner wall design of Sceedule 40 Carbon Steel Pipe provides a larger internal diameter, allowing higher flow capacity. Schedule 80 pipe reduces internal diameter slightly, affecting fluid velocity.
Engineers calculate pressure drops and flow efficiency for each application. Choosing the right pipe schedule helps ensure stable performance. It also supports safety standards and saves costs in HVAC, water supply, and chemical piping systems.
Comparing SCH 40 and SCH 80
Wall thickness is the main difference. SCH 80 walls are thicker, giving higher pressure tolerance and durability. Thicker walls slightly reduce the internal diameter, affecting flow.
A 2-inch SCH 40 pipe typically handles around 280 psi. The same size SCH 80 pipe supports about 400 psi. SCH 80 pipe has a higher weight and typically involves greater material cost.
Installation requires stronger supports. Fittings follow the same schedule rules. Pipe fittings manufactured to SCH 80 standards support higher operating pressures.
Both schedules come in carbon steel, stainless steel pipe, and PVC pipe. Choosing the right combination ensures safety, reliability, and compliance with industrial standards.
Inspection needs also differ. Schedule 80 pipe systems are designed for long-term operation with lower inspection frequency. SCH 40 pipe may require more frequent inspection in harsh conditions. Engineers consider these factors when planning maintenance schedules and life-cycle costs.
Installation Tips
Schedule 40 pipe is easier to cut, join, and support because it is lighter. Howevr SCH 80 pipe requires special cutting and welding tools.
Proper alignment and support prevent sagging or stress points.Thermal expansion is an important design consideration. SCH 80 pipe resists deformation under heat, but expansion joints may still be needed.
Proper installation improves system safety.It helps extend the overall service life of the system. Fluid transport remains stable in water supply, HVAC, and chemical pipeline systems.
Post time: Dec-26-2025