When it comes to modern steel pipe manufacturing, ERW (Electric Resistance Welding) and HFW (High-Frequency Welding) are two of the most common and efficient production methods.While they might appear identical at first glance, ERW and HFW steel pipes vary considerably in their welding methods, quality benchmarks, and application scopes. Understanding the difference between ERW and HFW steel pipes is essential for choosing the appropriate material for your project.
What Is ERW Pipe?
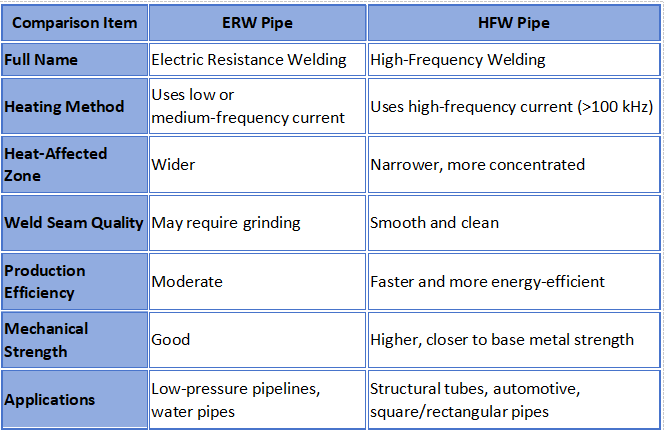
ERW (Electric Resistance Welding) pipes are made by rolling a steel coil into a cylindrical or square shape and then joining the edges by applying electrical current and mechanical pressure.
The heat produced by electrical resistance at the seam causes the steel edges to melt and merge, creating a continuous, solid weld.
ERW pipes are known for:
Strong dimensional precision
Consistent wall thickness
Cost efficiency for large-scale production
These pipes are widely used in water supply systems, low-pressure piping, and general structural applications.
What Is HFW Pipe?
HFW (High-Frequency Welding) pipe is a type of ERW pipe that uses high-frequency current (above 100 kHz) to heat and weld the steel edges.
In contrast to traditional ERW, which may rely on low-frequency current, HFW applies a focused, high-intensity heat to a limited area, ensuring a smaller heat-affected zone (HAZ) and superior weld integrity.
The process includes:
1.Shaping the steel strip into the required form (round, square, or rectangular).
2. Heating the edges via induction using a high-frequency current.
3.Pressure welding the heated edges to form a smooth, seamless joint.
HFW technology enables cleaner, more accurate welds with minimal oxidation , making it well-suited for high-strength structural steel tubes and precision square pipe.
Main Differences Between ERW and HFW Pipes
Technical Explanation
While both ERW and HFW rely on electrical resistance to produce heat, the specific current and frequency significantly influence the process.
ERW Welding Principle:
Low-frequency current flows through the steel strip, creating heat along the joint through resistance. The heated edges are then forced together to form a solid bond.
HFW Welding Principle:
Uses high-frequency induction to create intense, concentrated heat directly along the weld line. This yields a superior, more polished weld with very little material distortion.
Essentially, HFW represents a more sophisticated evolution of ERW, engineered to enhance weld integrity, production speed, and overall operational efficiency.
Applications of ERW and HFW Pipes
Both ERW and HFW pipes are used in a wide range of industries, but their applications differ depending on performance needs.
ERW Steel Pipes:
Water and gas pipelines
Scaffolding and fencing
Low-pressure transportation systems
General engineering structures
HFW Steel Pipes:
Steel structure and building frames
Square and rectangular hollow sections
Automotive and machinery manufacturing
Greenhouses, furniture, and precision construction
Since HFW pipes can achieve high weld strength and dimensional accuracy, they are often preferred in modern construction and mechanical engineering applications.
Surface Treatment Options
Both ERW and HFW pipes are available in different surface finishes:
Black (untreated): Natural dark surface, used for indoor or non-corrosive environments.
Hot-dip galvanized: Zinc coating offers enhanced corrosion resistance ,ideal for outdoor or water-exposed ssytems.
Pre-painted or powder-coated: Used for aesthetic appeal or to provide extra protection against rust.
Tianjin Yuantai Derun Group, supply both black HFW square pipes and galvanized steel tubes to meet diverse application requirements.
For projects that call for high-strength structural tubing or precision square pipes, selecting HFW welded pipes will ensure a longer service life and better performance than conventional ERW pipes.
Post time: Nov-07-2025