Pipes play a vital role in industrial systems. They transport liquids and gases and support mechanical structures. Industries such as oil and gas, construction, and equipment manufacturing rely on them daily.
Manufacturers use different production methods. These methods create differences in pipe structure and performance.These differences affect strength, precision, and cost effective.
Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) steel pipes and Drawn Over Mandrel (DOM) pipes are two widely used examples. Each type serves specific working conditions.Understanding their differences helps engineers make safer and more efficient choices.
What Is an ERW Pipes?
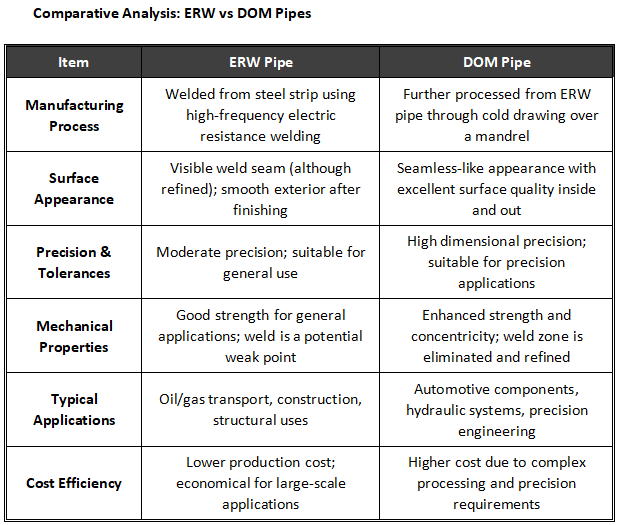
An ERW pipe’s raw material is steel strip. Manufacturers form the strip into a round shape and weld it along the seam. High-frequency electric resistance heats the edges of the steel. Pressure then joins them without filler metal.
This process creates a continuous weld. After finishing, the seam becomes narrow and smooth.
Key Advantages of ERW Pipes
ERW pipes can be produced efficiently.This approach keeps production costs relatively low and supports large-scale manufacturing.
Their dimensions are consistent and suitable for standard applications.
The internal surface is smooth, which helps reduce fluid resistance.
The finished appearance is clean and uniform.
Typical Uses
Industries widely use ERW pipes in oil and gas transportation systems. Builders use them in building structures, scaffolding systems, and general machinery.
What Is a DOM Pipe?
Manufacturing a DOM pipe involves taking an ERW pipe and subjecting it to additional cold drawing and sizing operations. It undergoes cold drawing through a die and over a mandrel. This process removes internal weld flash. It also improves accuracy and surface quality.
DOM pipes are usually made from 1020 or 1026 carbon steel. Although they start as welded tubes, their final form closely resembles seamless pipe.
Key Advantages of DOM Pipes
Manufacturers maintain tight dimensional tolerances.
Both inner and outer surfaces are smooth and uniform.
Mechanical properties improve after cold working.
Roundness and centrality are significantly enhanced.
Typical Uses
DOM pipes are widely used in automotive parts. Common examples include drive shafts and shock absorber cylinders. They are also used in hydraulic systems and precision machinery.
ERW Pipe vs DOM Pipe: A Comparison
Manufacturing Method
Manufacturers fabricate ERW pipes by forming steel strips and welding the seam.
DOM pipes result from cold-drawing ERW pipes to achieve precise dimensions and improved properties.
Surface Quality
The weld seam on ERW pipes is typically well-defined and refined.
“DOM pipes feature a nearly seamless finish, both internally and externally.
Dimensional Accuracy
ERW pipes provide moderate precision.
DOM pipes offer high accuracy for demanding applications.
Mechanical Performance
ERW pipes provide reliable strength for general use.
DOM pipes show improved strength and better structural evenness.
Applications
ERW pipes suit structural and transport purposes.
DOM pipes are preferred for high-precision mechanical components.
Cost Considerations
ERW pipes are more economical for large projects.
DOM pipes cost more because of extra processing and tighter controls.
Conclusion
ERW and DOM pipes each serve important industrial roles. ERW pipes make a balance between performance and cost well. They work effectively in general construction and transport systems.
DOM pipes focus on precision and strength. They are better suited for high-performance and safety-critical parts.
The final choice should reflect project needs. Pressure limits, tolerance requirements, surface quality, and budget all matter.
Post time: Dec-26-2025